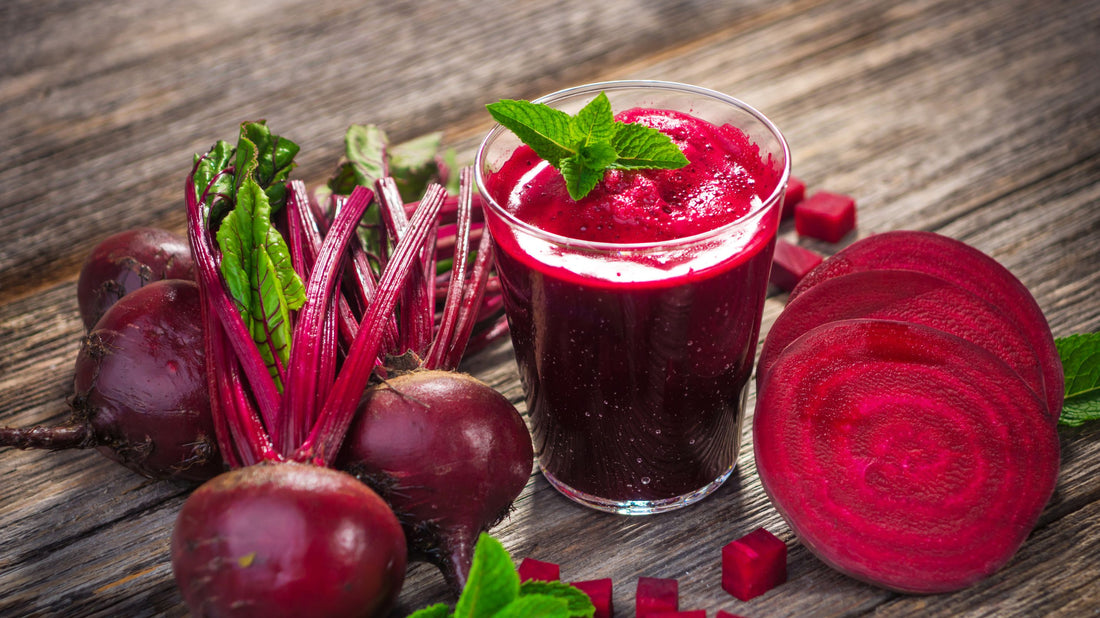
Beets, with their vibrant colour and earthy flavour, are more than just a striking addition to your plate. These root vegetables are nutritional powerhouses, packed with essential vitamins, minerals, and compounds that offer numerous health benefits. Moreover, beets are high in fiber, which supports digestive health. Here are the top three benefits of incorporating beets into your diet!
#1: Betalains: The Antioxidant Heroes in Beets
First up on the list are betalains. These are the pigments responsible for the beautiful red and yellow hues of beets. But betalains are more than just a pretty colour—they’re potent antioxidants that can help protect your cells from damage.
In North America, the availability of betalain-rich foods is quite limited, with red beets being one of the few common sources.[i] So, every time you enjoy beets, you’re giving your body a crucial source of these essential compounds.
#2: Nitrates: Nature’s Boost for Your Heart and Performance
Beets are loaded with nitrates, which your body converts into nitric oxide—a molecule that helps dilate blood vessels and improve blood flow. This is particularly beneficial for heart health. Improved blood flow can lower blood pressure, reducing the risk of heart disease.[vii]
#3: Clinical Effectiveness: The Beet's Secret to Overall Health
Research indicates that the antioxidant properties of betalains may help reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the body, which are linked to chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer.[ii] Additionally, studies have shown that taking 12.5 mg of betalains twice a day can improve exercise performance and recovery in competitive athletes. [iii] [iv]
The nitrates in beets can also enhance athletic performance. Research indicates that consuming beet juice before exercise can increase stamina and improve oxygen use in muscles, making it a favourite among athletes.[v] [vi] So, if you're looking to boost your workout, beets might be your new best friend.
Experience the Benefits of Beet+Haskap
Excited to experience the benefits of beets firsthand? Why not give our Beet+Haskap Super Shot a try! This powerful blend of beets and haskap berries combines the betalain-packed goodness of beets with the anthocyanin-rich haskap berries, creating a super shot that’s a fantastic addition to any diet, helping you stay nourished and healthy from the inside out. Just a quick shot each day can help you feel more energized and nourished.
References:
[i] Esquivel, P. (2016). Betalains. In Handbook on Natural Pigments in Food and Beverages. ScienceDirect.
[ii] Kanner, J., Harel, S., & Granit, R. (2001). Betalains—a new class of dietary cationized antioxidants. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 49(11), 5178–5185.
[iii] Van Hoorebeke, J. S., Trias, C. O., Davis, B. A., Lozada, C. F., & Casazza, G. A. (2016). Betalain-rich concentrate supplementation improves exercise performance in competitive runners. Nutrients, 8(9), 531.
[iv] Montenegro, C. F., Kwong, D. A., Minow, Z. A., Davis, B. A., Lozada, C. F., & Casazza, G. A. (2016). Betalain-rich concentrate supplementation improves exercise performance and recovery in competitive triathletes. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 41(10), 1020-1028.
[v] Lansley, K. E., Winyard, P. G., Fulford, J., Vanhatalo, A., Bailey, S. J., Blackwell, J. R., ... & Jones, A. M. (2011). Dietary nitrate supplementation reduces the O2 cost of walking and running: a placebo-controlled study. Journal of Applied Physiology, 110(3), 591–600.
[vi] Clifford, T., Howatson, G., West, D. J., & Stevenson, E. J. (2015, April 14). The potential benefits of red beetroot supplementation in Health and Disease. The Potential Benefits of Red Beetroot Supplementation in Health and Disease.
[vii] Webb, A. J., Patel, N., Loukogeorgakis, S., Okorie, M., Aboud, Z., Misra, S., ... & Ahluwalia, A. (2008). Acute blood pressure lowering, vasoprotective, and antiplatelet properties of dietary nitrate via bioconversion to nitrite. Hypertension, 51(3), 784–790.